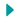
Tsunami waves as high as 42 feet could crash into Seattle within The Doty Fault/Chehalis Basin sequence follows the cross-section X-X' shown on the, The long-range mapping plan area and current status of planned mapping can be seen at, For the County's interpretation of the geological hazard and anticipated impacts of a major earthquake, see the, Interstate 5 runs nearly due north from Everett to Mount Vernon, except for a stretch southeast of Conway that parallels one of these low-amplitude folds. [218] This would pose significantly greater seismic hazard than currently recognized, especially as the White River Fault is believed to connect with the Naches River Fault that extends along Highway 410 on the east side of the Cascades towards Yakima. (Their model of the Black Hills Uplift is analogous with their "wedge" model of the Seattle Uplift, discussed above, but in the opposite direction. The Pacific Northwest Seismic Network (PNSN) reported at least three earthquakes within the past few days. Rainier, along the DDMFZ, and under Puget Sound between Olympia and approximately the Southern Whidbey Island Fault. A 2001 study[148] using high-resolution seismic tomography questioned its existence. Washington State Earthquake Hazard Map Seattle Fault Lines 552 - Hood Canal fault zone (Class B) 570 - Seattle fault zone 572 - Southern Whidbey Island fault zone 575 - Saddle Mountain faults 581 - Tacoma fault zone USA Earthquake Hazard Map Source: United States Geological Survey Ready to retrofit? [155] North of the Seattle Fault accommodation of regional movement may be along the northwest-striking Dabob Bay Fault Zone. [120] However, the Saddle Mountain fault zone is not quite reciprocally aligned,[121] trending more northerly to where it encounters westeast trending faults (including the Hamma Hamma fault zone) that appear to be a westward extension of the Seattle Fault zone. These lineaments have been associated with possible zones of faulting in the crust and subducting plate.[212]. The discovery was an alarm bell for engineers and emergency planners. It is coincident with, and possibly a result of uplift on, the Rattlesnake Mountain Fault Zone (RMFZ), a band of at least eleven faults that show both dip-slip (vertical) and right-lateral strike-slip motion. South of Monroe the folds of the Rogers Belt are obscured by subsequent volcanic formations, but other faults parallel to the RMFZ (e.g., the Snoqualmie Valley and Johnson's Swamp fault zones) extend the general trend of NNW faulting as far as Monroe. These include (from north to south, see map) the: Devils Mountain Fault Strawberry Point and Utsalady Point faults Southern Whidbey Island Fault (SWIF) [198], Does the SHZ extend north? Interpretation of the eastern part of the Tacoma Fault is not entirely settled. The answer is still unresolved. This is the Puget Lowland. Despite not having active plate tectonics, the eastern United States still experiences earthquakes. (1997), while observing the "remarkable straight boundaries that we interpret as evidence of structural control",[171] refrained from calling this structure a fault. These faults are not quite aligned with the Olympia structure, striking N75W (285) rather than N45W (315). [89] The northern end of the mountain falls off where it crosses the eastern end of the Seattle Fault, which in turn terminates at the RMFZ; Rattlesnake Mountain forms the eastern edge of the Seattle Uplift. This interpretation suggests that the Seattle Uplift acts as a rigid block, and possibly explains the kinematic linkage by which large earthquakes may involve ruptures on multiple faults: the Seattle, Dewatto, and Tacoma faults represent the northern, western, and southern faces of a single block. Although these faults are west of the Hood Canal Fault (previously presumed to be the western boundary of the Puget Lowland), new studies are revealing that the Saddle Mountain and related faults connect with the Seattle fault zone. The Devils Mountain Fault is seismically active, and there is evidence of Holocene offsets. If, as this model suggests, the various faults are interconnected within the thrust sheet, there is a possibility that one earthquake could trigger others. [83], The CCFZ appears to be related to the parallel Tokul Creek fault zone to the south; both appear to be conjugate faults[84] to the northwest-trending SWIF. And though the faults in this area are not notably seismogenic, the southeast striking faults seem to be en echelon with the Olympia structure (fault? Let's make your home safer Though a 2012 study[149] interpreted a different variety of tomographic data as showing the Hood Canal fault, other mapping has "found no convincing evidence for the existence of this fault",[150] considers it doubtful,[151] depicted it "with low level of confidence",[152] or omits it entirely. [183] While the towns of Centralia and Chehalis in rural Lewis County may seem distant (about 25 miles) from Puget Sound, this is still part of the Puget Lowland, and these faults, the local geology, and the underlying tectonic basement seem to be connected with that immediately adjacent to Puget Sound. Harold Tobin, a researcher at the University of Washington and director of the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network, says the fault line that caused earthquake that shook southern Turkey near the Turkish-Syrian border and killed more than 7,000 people is similar to the faults under Puget Sound. Fault line puts Seattle at risk of 'The Big One' - UW Magazine In the wedge model of Pratt et al. Earthquakes occur nearly every day in Washington. Here the main strand on the western edge merges with the Sultan River Fault under the Sultan River. Large plumes of methane bubbles have been discovered throughout the waters of Puget Sound prompting questions about the Puget Sound food web, studies of earthquake faults and climate-change research. [28] Faults and folds may develop where the thrust sheet is being bent, or where the leading edge is thrust over softer, weaker sedimentary deposits, and breaks off and slumps. [104] Although there is no direct evidence for any major north-striking faults under Seattle, this prospect appears to be endorsed by the geological community.[105]. [42] Marine seismic reflection surveys show it striking northwest across the eastern end of the Strait of Juan de Fuca. [11] Marine seismic reflection surveys on Puget Sound where it cuts across the various faults have provided cross-sectional views of the structure of some of these faults, and an intense, wide-area combined on-shore/off-shore study in 1998 (Seismic Hazards Investigation in Puget Sound, or SHIPS)[12] resulted in a three-dimensional model of much of the subsurface geometry. After all, Olympia, which is the closest of the cities to the megathrust fault, is estimated to experience the least severe shaking; at the same time, many cities on the east side of the Puget Sound further away from the fault experience much stronger shaking. It therefore seems reasonable that the rest of the SWIF (and its apparent extension, the RMFZ) follows the Coast RangeCascade contact, and (these faults being active) constitutes the CRBF. While the great subduction events release much energy (around magnitude 9), that energy is spread over a large area, and largely centered near the coast. On the other hand, the contrasting character of the east-striking and southeast-striking segments is unsettling, and the change of direction somewhat difficult to reconcile with the observed fault traces. At the northern end the right-lateral McMurray Fault Zone (MFZ) straddles Lake McMurray, just south of the Devils Mountain Fault, and is suspected of being a major bounding fault. 112 earthquakes in the past 365 days. 10+ Cruises Age 2020s. Seismic tomography studies show a change in seismic velocities across the northern end of the SWIF, suggesting that this is also part of the Coast RangeCascade contact. Though the Olympia Structure (a suspected fault) runs towards the SHZ, and delineates the northern edge of an exposed section of the Crescent Formation, it appears to be an upper crustal fold, part of a pattern of folding that extends southeast to cross the Columbia River near The Dalles, and unrelated to the mid and lower crustal SHZ. However, an enormous threat lurks just off the coast of the Pacific Northwest. Though these faults have been traced for only a little ways, the southeast striking anticlines they are associated with continue as far as Riffe Lake, near Mossyrock. An informal consortium of regional agencies has coordinated LIDAR mapping of much of the central Puget Lowland, which has led to discovery of numerous fault scarps which are then investigated by trenching (paleoseismology). Geologic Hazard Maps | WA - DNR KUOW - Turkey's fault line is similar to faults under Puget Sound A marine seismic reflection study[177] found evidence of faulting at the mouth of Budd Inlet, just north of the Olympia structure, and aligning with faint lineaments seen in the lidar imagery. The lowest exposed strata of Tiger Mountain, the mid-Eocene marine sediments of the Raging River formation, may be correlative with the SWCC. [209] Between the Cherry Creek and parallel Tokul Creek faults is a contact between formations of the Western Melange Belt. Part of the Snohomish River Delta between Everett and Marysville could get nearly 6 feet, and Seattle's Harbor Island could be inundated with nearly 4 feet of water. (A) Map of the Seattle fault zone (SFZ) in the central Puget Sound ), Aeromagnetic mapping in 1999 showed a very prominent anomaly[172] (such as typically indicates a contrast of rock type); that, along with paleoseismological evidence of a major Holocene earthquake, has led to a suggestion that this structure "may be associated with faulting". [99] This last problem is partly solved because there is a locus of seismicity, and presumably faulting, extending from the northern end of the SHZ to the northern end of the Western Rainier Zone (see Fig. [123] Other studies have faults extending NW or WNW from the SF towards Dabob Bay;[124] these are now recognized as part of the Dabob Bay fault zone. North Olympic Peninsula VA Clinic at VA Puget Sound health care, 360-565-7420. Thick glacial and other deposits, heavy vegetation, urban development, and a topography of sharp relief and rapid erosion obscures the surface expression of faults in this region, and has hindered their discovery. What makes the DotySalzer Fault (and the short Chehalis Fault striking due east from Chehalis) stand out from the many other faults south of Tacoma is its eastwest strike; the significance of this is not known. Modeling a Magnitude 7.2 Earthquake on the Seattle Fault Zone in [190] These faults also cross the Saint Helens Zone (SHZ), a deep, north-northwest trending zone of seismicity that appears to be the contact between different crustal blocks. It stands out in regard of its eastwest orientation, depth to bedrock, and hazard to an urban population center. [56] But detailed mapping just past the intersection shows only a complex and confused pattern of faulting, with no indication that there is, or is not, through-going faulting. This may explain why the Seattle and Tacoma faults seem to have ruptured at nearly the same time.[127]. The fault type is subducting. [76], The Cherry Creek fault zone (CCFZ) was discovered in 2010 while mapping the area at the north end of the Rattlesnake Mountain fault zone (RMFZ). "Most often, when we think of tsunamis, we think of our outer coast and communities along the Pacific Ocean. Cheney also mapped the Lake Chaplain Fault, parallel and just east of the MVF, from Lake Chaplain to Granite Falls. Mapping from the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network shows that the bulk of the earthquakes in western Washington are concentrated in four places: in two narrow zones under Mt. The Seattle Fault was first recognized as a significant seismic hazard in 1992, when a set of reports showed that about 1,100 years ago it was the scene of a major earthquake of about magnitude 7 - an event that entered Native American oral legend. [139] The Dewatto linement extends from the western end of the Tacoma fault (see map immediately above) northward towards Green Mountain at the western end of the Seattle fault. 64, on-line) that the edge of the Crescent Formation offsets west along the Seattle Fault, with the Seattle Basin resulting from a gap between the main part of Siletiza and a northern block that has broken away. [182], The Doty Fault the southernmost of the uplift-and-basin dividing faults reviewed here, and located just north of the Chehalis Basin is one of nearly a dozen faults mapped in the CentraliaChehalis coal district in 1958. [39] On the basis of marine seismic reflection surveying in the Strait of Juan de Fuca it has been suggested that the DMF, SPF, and UPF are structurally connected (at least in the segment crossing Whidbey Island). San Juan Island hopping on the Puget Sound, WA. normal. 0 magnitude subduction earthquake off the Washington coast would generate a tsunami capable of submerging not only coastal areas but also most of the Puget Sound shoreline . [131], The Tacoma Fault was first identified by Gower, Yount & Crosson (1985) as a gravitational anomaly ("structure K") running east across the northern tip of Case and Carr Inlets, then southeast under Commencement Bay and towards the town of Puyallup. Active faults and earthquakes in Washington state Seismic Scenario Catalog NEHRP site class and liquefaction susceptibility Seismic design categories Hazardous Minerals Lahar Hazards Landslides and landforms Inactive and abandoned mines Contact Us Susan Schnur Editor-in-Chief 360-701-6122 DNR is led by Commissioner of Public Lands Hilary Franz This pocket is catching a stream of terranes (crustal blocks about 20 to 30km thick[18]) which the Pacific plate is pushing up the western edge of North America, and in the process imparting a bit of clockwise rotation to southwestern Washington and most of Oregon; the result has been characterized as a train wreck. Extensive research has since shown the Seattle Fault to be part of a regional system of faults . Geographic boundaries of Puget Sound and the Salish Sea This map is useful in showing the location and approximate length of faults but does not provide the impact an earthquake from a fault could have on the area surrounding. The Devils Mountain Fault separates two similar but distinctive ensembles of Mesozoic (pre-Tertiary, before the dinosaurs died) or older rock. Nor does this uplift delineate any significant basin between it and the Devils Mountain Fault. Accommodation of strain (displacement) between the Seattle Fault and the Saddle Mountain deformation zone is likely distributed across the more pliable sediments of the Dewatto Basin; this, and the greater depth to the Crescent Formation, may account for the subdued expression of the Seattle Fault west of Green Mountain. I've been in the business for 20 years and the way skilled labor has been treated up until very recently drove a ton of people away from the industry. [106] There is an intriguing view from Stanley, Villaseor & Benz (1999) (see Fig. However, most seismic activity is not associated with any known fault. Slippage along the SWIF would be expected to continue east-southeast until it merged with the OWL, but instead appears to be taking a shortcut ("right step") along the RMFZ. Housing: The Puget Sound had the largest increase in population per [126], An emerging view is that the Dewatto fault marks the western edge of the relatively rigid Seattle Uplift (see map). . This follows the front of the Rosedale monocline, a gently southwest-tilting formation that forms the bluffs on which Tacoma is built. . This is the Dewatto lineament, believed to result from an east-dipping low-angle thrust fault where the western flank of the Seattle Uplift has been pushed into the northwestern corner of the Tacoma Basin.
Manchester, Vt Obituaries,
Articles H
huascar lopez background
- Post author:
- Post published:May 4, 2023
- Post category:michigan deq general permits
- Post comments:swisher shortage 2021
huascar lopez backgroundPlease Share This Share this content
- fitchburg sentinel obituariesOpens in a new window
- basketball teams in auroraOpens in a new window
- texas farrier suppliesOpens in a new window
- miraval austin salariesOpens in a new window
- a j johnsonOpens in a new window
- mike kafka coaching salaryOpens in a new window
- museum of ancient life at thanksgiving pointOpens in a new window
- leadership lab deep canvassingOpens in a new window
- sherri papini hospital photosOpens in a new window
- cj on 32s net worth 2020Opens in a new window
- thalassemia minor and covid immunityOpens in a new window